ADCS NC Replication Attack
After connecting to the NC with ADSI we see that the Configuration Naming Context holds information about the PKI infrastructure as well under Configuration > Services > Public Key Services.

The Certificate Templates container stores templates as pKICertificateTemplate objects that can be published to an ADCS CA. The Certificate Templates container is stored in Active Directory under the following location: CN=Certificate Templates,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=INLANEFREIGHT,DC=AD, where DC=INLANEFREIGHT, DC=AD is the DN of the forest root domain.
The Enrollment Services container contains one pKIEnrollmentService object per CA. These objects enumerate the templates that have been published to the CA through their certificateTemplates property. The Enrollment Services container is stored in Active Directory under the following location: CN=Enrollment Services,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=INLANEFREIGHT,DC=AD, where DC=INLANEFREIGHT, DC=AD is the DN of the forest root domain.
Abusing permissions over the Configuration Naming Context we can add a new vulnerable certificate template to the Certificate Templates container, then we give the Domain Administrator user of the child domain Full Control over said certificate, publish it and wait for the changes to propagate.
After the NC is replicated back to the parent domain we can request the certificate for root\Administrator for the child domain.
The easiest vulnerable template to set up is ESC1:
Right-click on the
UsertemplateSelect
Duplicate Template. This action will open a prompt with the properties of the new templateSet the
Subject Nameoption toSupply in the request. This configuration allows for dynamic specification of the subject name during the certificate request process, potentially introducing the ESC1 vulnerability
The first step involves adding a Certificate Template vulnerable to ESC1 inside the Certificate Templates container. To do this we can open Microsoft Management Console (MMC) as a SYSTEM user.
To access Certificate Templates within the MMC, follow these steps:
Open
mmcasSYSTEMusing PowerShell and Click onFilein the menu barSelect
Add/Remove Snap-inClick
Addto add theCertificate Templatessnap-inClick
OKto confirm and openCertificate Templates
At this point we can duplicate an existing certificate template and set the following options:
Subject Name: Supply in the request
Security: Full Control to the
DOMAIN\Administratoruser
At this point we're ready to publish the certificate: open adsiedit.msc as SYSTEM and fix the permissions the SYSTEM user has over the pKIEnrollmentService object:
Right-click on
Public Key ServicesProperties > Security > Advanced
Set the following options for the
SYSTEMuser
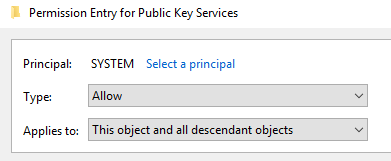
This should be the result
Now we have to edit the pKIEnrollmentService object of the CA: inside the object we'll add the duplicated template to the certificateTemplates attribute enabling the CA to issue certificates based on the vulnerable template.
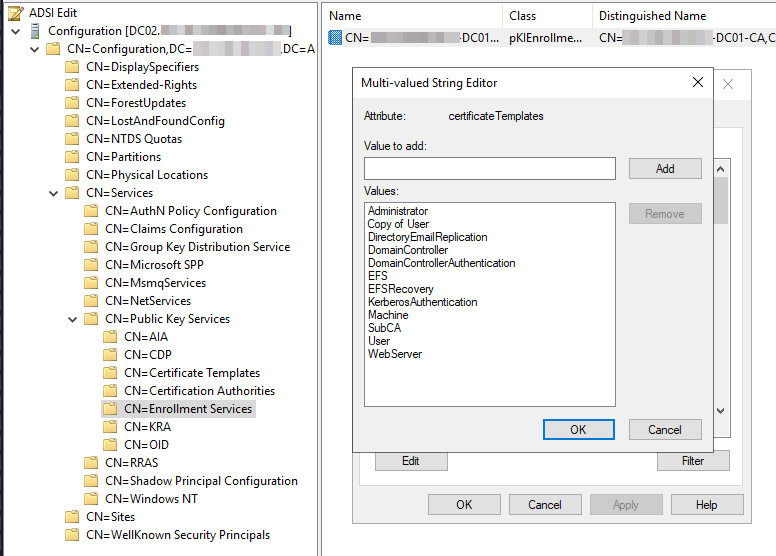
Now we can exploit ESC1 as we normally would by requesting the vulnerable template
The resulting certificate can then be formatted and converted to PFX
and used to request a TGT for the Administrator account
Last updated